2024
Rahaman, N., Weiss, M., Wüthrich, M., Bengio, Y., Li, E., Pal, C., Schölkopf, B.
Language Models Can Reduce Asymmetry in Information Markets
arXiv:2403.14443, March 2024, Published as: Redesigning Information Markets in the Era of Language Models, Conference on Language Modeling (COLM) (techreport)
2023
Jin, Z., Mihalcea, R.
Natural Language Processing for Policymaking
In Handbook of Computational Social Science for Policy, pages: 141-162, 7, (Editors: Bertoni, E. and Fontana, M. and Gabrielli, L. and Signorelli, S. and Vespe, M.), Springer International Publishing, 2023 (inbook)
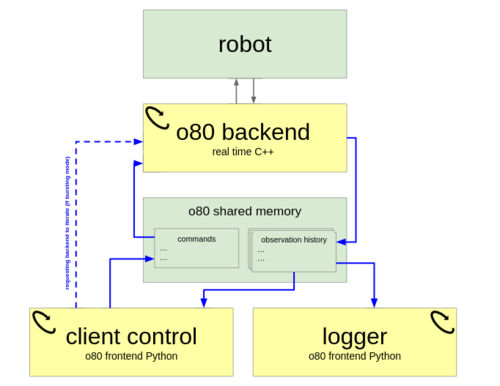
Berenz, V., Widmaier, F., Guist, S., Schölkopf, B., Büchler, D.
Synchronizing Machine Learning Algorithms, Realtime Robotic Control and Simulated Environment with o80
Robot Software Architectures Workshop (RSA) 2023, ICRA, 2023 (techreport)
2022
Biester, L., Demszky, D., Jin, Z., Sachan, M., Tetreault, J., Wilson, S., Xiao, L., Zhao, J.
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact (NLP4PI)
Association for Computational Linguistics, December 2022 (proceedings)
Schölkopf, B., Uhler, C., Zhang, K.
Proceedings of the First Conference on Causal Learning and Reasoning (CLeaR 2022)
177, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, PMLR, April 2022 (proceedings)
Peters, J., Bauer, S., Pfister, N.
Causal Models for Dynamical Systems
In Probabilistic and Causal Inference: The Works of Judea Pearl, pages: 671-690, 1, Association for Computing Machinery, 2022 (inbook)
Karimi, A. H., von Kügelgen, J., Schölkopf, B., Valera, I.
Towards Causal Algorithmic Recourse
In xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI: International Workshop, Held in Conjunction with ICML 2020, July 18, 2020, Vienna, Austria, Revised and Extended Papers, pages: 139-166, (Editors: Holzinger, Andreas and Goebel, Randy and Fong, Ruth and Moon, Taesup and Müller, Klaus-Robert and Samek, Wojciech), Springer International Publishing, 2022 (inbook)
Salewski, L., Koepke, A. S., Lensch, H. P. A., Akata, Z.
CLEVR-X: A Visual Reasoning Dataset for Natural Language Explanations
In xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI: International Workshop, Held in Conjunction with ICML 2020, July 18, 2020, Vienna, Austria, Revised and Extended Papers, pages: 69-88, (Editors: Holzinger, Andreas and Goebel, Randy and Fong, Ruth and Moon, Taesup and Müller, Klaus-Robert and Samek, Wojciech), Springer International Publishing, 2022 (inbook)
Schölkopf, B.
Causality for Machine Learning
In Probabilistic and Causal Inference: The Works of Judea Pearl, pages: 765-804, 1, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 2022 (inbook)
2021
Field, A., Prabhumoye, S., Sap, M., Jin, Z., Zhao, J., Brockett, C.
Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact
Association for Computational Linguistics, August 2021 (proceedings)
Belousov, B., H., A., Klink, P., Parisi, S., Peters, J.
Reinforcement Learning Algorithms: Analysis and Applications
883, Studies in Computational Intelligence, Springer International Publishing, 2021 (book)
Scientific Report 2016 - 2021
2021 (mpi_year_book)
2019
Scientific Report 2016 - 2018
2019 (mpi_year_book)
2018
Schölkopf, B.
Maschinelles Lernen: Entwicklung ohne Grenzen?
In Mit Optimismus in die Zukunft schauen. Künstliche Intelligenz - Chancen und Rahmenbedingungen, pages: 26-34, (Editors: Bender, G. and Herbrich, R. and Siebenhaar, K.), B&S Siebenhaar Verlag, 2018 (incollection)
Wichmann, F. A., Jäkel, F.
Methods in Psychophysics
In Stevens’ Handbook of Experimental Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience, 5 (Methodology), 7, 4th, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2018 (inbook)
Jayaram, V., Fiebig, K., Peters, J., Grosse-Wentrup, M.
Transfer Learning for BCIs
In Brain–Computer Interfaces Handbook, pages: 425-442, 22, (Editors: Chang S. Nam, Anton Nijholt and Fabien Lotte), CRC Press, 2018 (incollection)
2017
Peters, J., Lee, D., Kober, J., Nguyen-Tuong, D., Bagnell, J., Schaal, S.
Robot Learning
In Springer Handbook of Robotics, pages: 357-394, 15, 2nd, (Editors: Siciliano, Bruno and Khatib, Oussama), Springer International Publishing, 2017 (inbook)
Peters, J., Janzing, D., Schölkopf, B.
Elements of Causal Inference - Foundations and Learning Algorithms
Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series, The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017 (book)
Peters, J., Bagnell, J.
Policy Gradient Methods
In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining, pages: 982-985, 2nd, (Editors: Sammut, Claude and Webb, Geoffrey I.), Springer US, 2017 (inbook)
Flad, N., Fomina, T., Bülthoff, H. H., Chuang, L. L.
Unsupervised clustering of EOG as a viable substitute for optical eye-tracking
In First Workshop on Eye Tracking and Visualization (ETVIS 2015), pages: 151-167, Mathematics and Visualization, (Editors: Burch, M., Chuang, L., Fisher, B., Schmidt, A., and Weiskopf, D.), Springer, 2017 (inbook)
Peters, J., Tedrake, R., Roy, N., Morimoto, J.
Robot Learning
In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining, pages: 1106-1109, 2nd, (Editors: Sammut, Claude and Webb, Geoffrey I.), Springer US, 2017 (inbook)
Janzing, D.
Statistical Asymmetries Between Cause and Effect
In Time in Physics, pages: 129-139, Tutorials, Schools, and Workshops in the Mathematical Sciences, (Editors: Renner, Renato and Stupar, Sandra), Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2017 (inbook)
2016
Ihler, A. T., Janzing, D.
Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI)
pages: 869 pages, AUAI Press, June 2016 (proceedings)
Zhang, K., Hyvärinen, A.
Nonlinear functional causal models for distinguishing cause from effect
In Statistics and Causality: Methods for Applied Empirical Research, pages: 185-201, 8, 1st, (Editors: Wolfgang Wiedermann and Alexander von Eye), John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2016 (inbook)
Hohmann, M., Fomina, T., Jayaram, V., Widmann, N., Förster, C., Just, J., Synofzik, M., Schölkopf, B., Schöls, L., Grosse-Wentrup, M.
A cognitive brain–computer interface for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
In Brain-Computer Interfaces: Lab Experiments to Real-World Applications, 228(Supplement C):221-239, 8, Progress in Brain Research, (Editors: Damien Coyle), Elsevier, 2016 (incollection)
2015
Charpiat, G., Hofmann, M., Schölkopf, B.
Kernel methods in medical imaging
In Handbook of Biomedical Imaging, pages: 63-81, 4, (Editors: Paragios, N., Duncan, J. and Ayache, N.), Springer, Berlin, Germany, June 2015 (inbook)
O’Donnell, L. J., Schultz, T.
Statistical and Machine Learning Methods for Neuroimaging: Examples, Challenges, and Extensions to Diffusion Imaging Data
In Visualization and Processing of Higher Order Descriptors for Multi-Valued Data, pages: 299-319, (Editors: Hotz, I. and Schultz, T.), Springer, 2015 (inbook)
Abbott, T., Abdalla, F. B., Allam, S., Amara, A., Annis, J., Armstrong, R., Bacon, D., Banerji, M., Bauer, A. H., Baxter, E., others,
Cosmology from Cosmic Shear with DES Science Verification Data
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05552, 2015 (techreport)
Jarvis, M., Sheldon, E., Zuntz, J., Kacprzak, T., Bridle, S. L., Amara, A., Armstrong, R., Becker, M. R., Bernstein, G. M., Bonnett, C., others,
The DES Science Verification Weak Lensing Shear Catalogs
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05603, 2015 (techreport)
Janzing, D., Steudel, B., Shajarisales, N., Schölkopf, B.
Justifying Information-Geometric Causal Inference
In Measures of Complexity: Festschrift for Alexey Chervonenkis, pages: 253-265, 18, (Editors: Vovk, V., Papadopoulos, H. and Gammerman, A.), Springer, 2015 (inbook)
2014
Kober, J., Peters, J.
Learning Motor Skills: From Algorithms to Robot Experiments
97, pages: 191, Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, Springer, 2014 (book)
Schultz, T., Nedjati-Gilani, G., Venkataraman, A., O’Donnell, L., Panagiotaki, E.
Computational Diffusion MRI and Brain Connectivity
pages: 255, Mathematics and Visualization, Springer, 2014 (book)
Zhang, K., Schölkopf, B., Muandet, K., Wang, Z., Zhou, Z., Persello, C.
Single-Source Domain Adaptation with Target and Conditional Shift
In Regularization, Optimization, Kernels, and Support Vector Machines, pages: 427-456, 19, Chapman & Hall/CRC Machine Learning & Pattern Recognition, (Editors: Suykens, J. A. K., Signoretto, M. and Argyriou, A.), Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, USA, 2014 (inbook)
Schultz, T., Fuster, A., Ghosh, A., Deriche, R., Florack, L., Lim, L.
Higher-Order Tensors in Diffusion Imaging
In Visualization and Processing of Tensors and Higher Order Descriptors for Multi-Valued Data, pages: 129-161, Mathematics + Visualization, (Editors: Westin, C.-F., Vilanova, A. and Burgeth, B.), Springer, 2014 (inbook)
Schultz, T., Vilanova, A., Brecheisen, R., Kindlmann, G.
Fuzzy Fibers: Uncertainty in dMRI Tractography
In Scientific Visualization: Uncertainty, Multifield, Biomedical, and Scalable Visualization, pages: 79-92, 8, Mathematics + Visualization, (Editors: Hansen, C. D., Chen, M., Johnson, C. R., Kaufman, A. E. and Hagen, H.), Springer, 2014 (inbook)
Sra, S.
Nonconvex Proximal Splitting with Computational Errors
In Regularization, Optimization, Kernels, and Support Vector Machines, pages: 83-102, 4, (Editors: Suykens, J. A. K., Signoretto, M. and Argyriou, A.), CRC Press, 2014 (inbook)
Balcan, M., Urner, R.
Active Learning - Modern Learning Theory
In Encyclopedia of Algorithms, (Editors: Kao, M.-Y.), Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2014 (incollection)
2013
Grosse-Wentrup, M., Schölkopf, B.
A Review of Performance Variations in SMR-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
In Brain-Computer Interface Research, pages: 39-51, 4, SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering, (Editors: Guger, C., Allison, B. Z. and Edlinger, G.), Springer, 2013 (inbook)
Schölkopf, B., Janzing, D., Peters, J., Sgouritsa, E., Zhang, K., Mooij, J.
Semi-supervised learning in causal and anticausal settings
In Empirical Inference, pages: 129-141, 13, Festschrift in Honor of Vladimir Vapnik, (Editors: Schölkopf, B., Luo, Z. and Vovk, V.), Springer, 2013 (inbook)
Sra, S.
Tractable large-scale optimization in machine learning
In Tractability: Practical Approaches to Hard Problems, pages: 202-230, 7, (Editors: Bordeaux, L., Hamadi , Y., Kohli, P. and Mateescu, R. ), Cambridge University Press , 2013 (inbook)
Hennig, P.
Animating Samples from Gaussian Distributions
(8), Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Tübingen, Germany, 2013 (techreport)
Deisenroth, M., Szepesvári, C., Peters, J.
Proceedings of the 10th European Workshop on Reinforcement Learning, Volume 24
pages: 173, JMLR, European Workshop On Reinforcement Learning, EWRL, 2013 (proceedings)
Hogg, D. W., Angus, R., Barclay, T., Dawson, R., Fergus, R., Foreman-Mackey, D., Harmeling, S., Hirsch, M., Lang, D., Montet, B. T., Schiminovich, D., Schölkopf, B.
Maximizing Kepler science return per telemetered pixel: Detailed models of the focal plane in the two-wheel era
arXiv:1309.0653, 2013 (techreport)
Montet, B. T., Angus, R., Barclay, T., Dawson, R., Fergus, R., Foreman-Mackey, D., Harmeling, S., Hirsch, M., Hogg, D. W., Lang, D., Schiminovich, D., Schölkopf, B.
Maximizing Kepler science return per telemetered pixel: Searching the habitable zones of the brightest stars
arXiv:1309.0654, 2013 (techreport)
Seldin, Y., Schölkopf, B.
On the Relations and Differences between Popper Dimension, Exclusion Dimension and VC-Dimension
In Empirical Inference - Festschrift in Honor of Vladimir N. Vapnik, pages: 53-57, 6, (Editors: Schölkopf, B., Luo, Z. and Vovk, V.), Springer, 2013 (inbook)
Schölkopf, B., Luo, Z., Vovk, V.
Empirical Inference - Festschrift in Honor of Vladimir N. Vapnik
Springer, 2013 (book)
2012
Grosse-Wentrup, M., Schölkopf, B.
High Gamma-Power Predicts Performance in Brain-Computer Interfacing
(3), Max-Planck-Institut für Intelligente Systeme, Tübingen, February 2012 (techreport)
Toussaint, M., Storkey, A., Harmeling, S.
Expectation-Maximization methods for solving (PO)MDPs and optimal control problems
In Inference and Learning in Dynamic Models, (Editors: Barber, D., Cemgil, A.T. and Chiappa, S.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, January 2012 (inbook) In press
Bruzzone, L., Persello, C., Demir, B.
Active Learning Methods in Classification of Remote Sensing Images
In Signal and Image Processing for Remote Sensing, (Editors: CH Chen), CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA, January 2012 (inbook) In press
Habeck, M.
Inferential structure determination from NMR data
In Bayesian methods in structural bioinformatics, pages: 287-312, (Editors: Hamelryck, T., Mardia, K. V. and Ferkinghoff-Borg, J.), Springer, New York, 2012 (inbook)