2024
Rahaman, N., Weiss, M., Wüthrich, M., Bengio, Y., Li, E., Pal, C., Schölkopf, B.
Language Models Can Reduce Asymmetry in Information Markets
arXiv:2403.14443, March 2024, Published as: Redesigning Information Markets in the Era of Language Models, Conference on Language Modeling (COLM) (techreport)
2023
Jenny, D.
Navigating the Ocean of Biases: Political Bias Attribution in Language Models via Causal Structures
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, November 2023, external supervision (thesis)
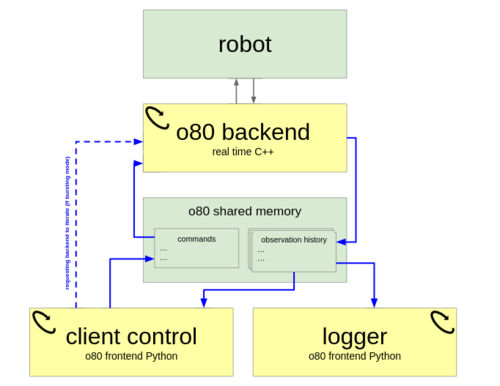
Berenz, V., Widmaier, F., Guist, S., Schölkopf, B., Büchler, D.
Synchronizing Machine Learning Algorithms, Realtime Robotic Control and Simulated Environment with o80
Robot Software Architectures Workshop (RSA) 2023, ICRA, 2023 (techreport)
2022
Schölkopf, B.
Causality, causal digital twins, and their applications
Machine Learning for Science: Bridging Data-Driven and Mechanistic Modelling (Dagstuhl Seminar 22382), (Editors: Berens, Philipp and Cranmer, Kyle and Lawrence, Neil D. and von Luxburg, Ulrike and Montgomery, Jessica), September 2022 (talk)
2021
Scientific Report 2016 - 2021
2021 (mpi_year_book)
2019
Safavi, S., Logothetis, N., Besserve, M.
Multivariate coupling estimation between continuous signals and point processes
Neural Information Processing Systems 2019 - Workshop on Learning with Temporal Point Processes, December 2019 (talk)
Lutz, P.
Automatic Segmentation and Labelling for Robot Table Tennis Time Series
Technical University Darmstadt, Germany, August 2019 (thesis)
Scientific Report 2016 - 2018
2019 (mpi_year_book)
2016
Castaneda, S., Katiyar, P., Russo, F., Calaminus, C., Disselhorst, J. A., Ziemann, U., Kohlhofer, U., Quintanilla-Martinez, L., Poli, S., Pichler, B. J.
Analysis of multiparametric MRI using a semi-supervised random forest framework allows the detection of therapy response in ischemic stroke
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2016 (talk)
Katiyar, P., Divine, M. R., Kohlhofer, U., Quintanilla-Martinez, L., Siegemund, M., Pfizenmaier, K., Kontermann, R., Pichler, B. J., Disselhorst, J. A.
Multi-view learning on multiparametric PET/MRI quantifies intratumoral heterogeneity and determines therapy efficacy
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2016 (talk)
2015
Besserve, M.
Causal Inference for Empirical Time Series Based on the Postulate of Independence of Cause and Mechanism
53rd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, September 2015 (talk)
Besserve, M.
Independence of cause and mechanism in brain networks
DALI workshop on Networks: Processes and Causality, April 2015 (talk)
Chaves, R., Majenz, C., Luft, L., Maciel, T., Janzing, D., Schölkopf, B., Gross, D.
Information-Theoretic Implications of Classical and Quantum Causal Structures
18th Conference on Quantum Information Processing (QIP), 2015 (talk)
Castaneda, S. G., Katiyar, P., Russo, F., Disselhorst, J. A., Calaminus, C., Poli, S., Maurer, A., Ziemann, U., Pichler, B. J.
Assessment of brain tissue damage in the Sub-Acute Stroke Region by Multiparametric Imaging using [89-Zr]-Desferal-EPO-PET/MRI
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2015 (talk)
Divine, M. R., Harant, M., Katiyar, P., Disselhorst, J. A., Bukala, D., Aidone, S., Siegemund, M., Pfizenmaier, K., Kontermann, R., Pichler, B. J.
Early time point in vivo PET/MR is a promising biomarker for determining efficacy of a novel Db(\alphaEGFR)-scTRAIL fusion protein therapy in a colon cancer model
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2015 (talk)
Abbott, T., Abdalla, F. B., Allam, S., Amara, A., Annis, J., Armstrong, R., Bacon, D., Banerji, M., Bauer, A. H., Baxter, E., others,
Cosmology from Cosmic Shear with DES Science Verification Data
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05552, 2015 (techreport)
Jarvis, M., Sheldon, E., Zuntz, J., Kacprzak, T., Bridle, S. L., Amara, A., Armstrong, R., Becker, M. R., Bernstein, G. M., Bonnett, C., others,
The DES Science Verification Weak Lensing Shear Catalogs
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05603, 2015 (techreport)
Foreman-Mackey, D., Hogg, D. W., Schölkopf, B.
The search for single exoplanet transits in the Kepler light curves
IAU General Assembly, 22, pages: 2258352, 2015 (talk)
2014
Besserve, M., Schölkopf, B., Logothetis, N. K.
Unsupervised identification of neural events in local field potentials
44th Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience (Neuroscience), 2014 (talk)
Besserve, M.
Quantifying statistical dependency
Research Network on Learning Systems Summer School, 2014 (talk)
Divine, M. R., Disselhorst, J. A., Katiyar, P., Pichler, B. J.
Using a population based Gaussian Mixture Model on fused [18]F-FDG PET and DW-MRI images accurately segments the tumor microenvironment into clinically relevant compartments capable of guiding therapy
European Molecular Imaging Meeting, 2014 (talk)
Janzing, D.
Causal Inference from Passive Observations
24th Summer School University of Jyväskylā, Finland, August, 2014 (talk)
2013
Logothetis, N., Eschenko, O., Murayama, Y., Augath, M., Steudel, T., Evrard, H., Besserve, M., Oeltermann, A.
Studying large-scale brain networks: electrical stimulation and neural-event-triggered fMRI
Twenty-Second Annual Computational Neuroscience Meeting (CNS*2013), July 2013, journal = {BMC Neuroscience},
year = {2013},
month = {7},
volume = {14},
number = {Supplement 1},
pages = {A1}, (talk)
Mantlik, F., Bezrukov, I., Hofmann, M., Schölkopf, B., Pichler, B.
MR-Based Attenuation Correction for Combined Brain PET/MR: Robustness of Atlas- and Pattern Recognition Method to Atlas Registration Failures
IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (IEEE MIC), 2013 (talk)
Hennig, P.
Animating Samples from Gaussian Distributions
(8), Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Tübingen, Germany, 2013 (techreport)
Muandet, K.
Domain Generalization via Invariant Feature Representation
30th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML2013), 2013 (talk)
Hogg, D. W., Angus, R., Barclay, T., Dawson, R., Fergus, R., Foreman-Mackey, D., Harmeling, S., Hirsch, M., Lang, D., Montet, B. T., Schiminovich, D., Schölkopf, B.
Maximizing Kepler science return per telemetered pixel: Detailed models of the focal plane in the two-wheel era
arXiv:1309.0653, 2013 (techreport)
Montet, B. T., Angus, R., Barclay, T., Dawson, R., Fergus, R., Foreman-Mackey, D., Harmeling, S., Hirsch, M., Hogg, D. W., Lang, D., Schiminovich, D., Schölkopf, B.
Maximizing Kepler science return per telemetered pixel: Searching the habitable zones of the brightest stars
arXiv:1309.0654, 2013 (techreport)
2012
Muandet, K.
Support Vector Machines, Support Measure Machines, and Quasar Target Selection
Center for Cosmology and Particle Physics (CCPP), New York University, December 2012 (talk)
Muandet, K.
Hilbert Space Embedding for Dirichlet Process Mixtures
NIPS Workshop on Confluence between Kernel Methods and Graphical Models, December 2012 (talk)
Wehrl, H., Lankes, K., Hossain, M., Bezrukov, I., Liu, C., Martirosian, P., Schick, F., Pichler, B.
Simultaneous small animal PET/MR in activated and resting state reveals multiple brain networks
20th Annual Meeting and Exhibition of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), May 2012 (talk)
Wehrl, H., Lankes, K., Hossain, M., Bezrukov, I., Liu, C., Martirosian, P., Reischl, G., Schick, F., Pichler, B.
A new PET insert for simultaneous PET/MR small animal imaging
20th Annual Meeting and Exhibition of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), May 2012 (talk)
Hossain, M., Wehrl, H., Lankes, K., Liu, C., Bezrukov, I., Reischl, G., Pichler, B.
Evaluation of a new, large field of view, small animal PET/MR system
50. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft fuer Nuklearmedizin (NuklearMedizin), April 2012 (talk)
Grosse-Wentrup, M., Schölkopf, B.
High Gamma-Power Predicts Performance in Brain-Computer Interfacing
(3), Max-Planck-Institut für Intelligente Systeme, Tübingen, February 2012 (techreport)
Muandet, K.
Support Measure Machines for Quasar Target Selection
Astro Imaging Workshop, 2012 (talk)
Seldin, Y.
PAC-Bayesian Analysis: A Link Between Inference and Statistical Physics
Workshop on Statistical Physics of Inference and Control Theory, 2012 (talk)
Liu, C., Hossain, M., Lankes, K., Bezrukov, I., Wehrl, H., Kolb, A., Judenhofer, M., Pichler, B.
PET Performance Measurements of a Next Generation Dedicated Small Animal PET/MR Scanner
Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS-MIC), 2012 (talk)
Wehrl, H., Hossain, M., Lankes, K., Liu, C., Bezrukov, I., Martirosian, P., Reischl, G., Schick, F., Pichler, B.
Simultaneous small animal PET/MR reveals different brain networks during stimulation and rest
World Molecular Imaging Congress (WMIC), 2012 (talk)
Seldin, Y., Laviolette, F., Shawe-Taylor, J.
PAC-Bayesian Analysis of Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning
Tutorial at the 29th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2012 (talk)
Bezrukov, I., Schmidt, H., Mantlik, F., Schwenzer, N., Brendle, C., Pichler, B.
Influence of MR-based attenuation correction on lesions within bone and susceptibility artifact regions
Molekulare Bildgebung (MoBi), 2012 (talk)
Boularias, A., Kroemer, O., Peters, J.
Structured Apprenticeship Learning
European Workshop on Reinforcement Learning (EWRL), 2012 (talk)
Seldin, Y., Laviolette, F., Shawe-Taylor, J.
PAC-Bayesian Analysis and Its Applications
Tutorial at The European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML-PKDD), 2012 (talk)
Deisenroth, M., Peters, J.
Solving Nonlinear Continuous State-Action-Observation POMDPs for Mechanical Systems with Gaussian Noise
European Workshop on Reinforcement Learning (EWRL), 2012 (talk)
Nishiyama, Y., Boularias, A., Gretton, A., Fukumizu, K.
Kernel Bellman Equations in POMDPs
Technical Committee on Infomation-Based Induction Sciences and Machine Learning (IBISML'12), 2012 (talk)
Panagiotaropoulos, T., Besserve, M., Logothetis, N.
Beta oscillations propagate as traveling waves in the macaque prefrontal cortex
42nd Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience (Neuroscience), 2012 (talk)
2011
Lois, C., Kupferschläger, J., Bezrukov, I., Schmidt, H., Werner, M., Mannheim, J., Pichler, B., Schwenzer, N., Beyer, T.
Combined whole-body PET/MR imaging: MR contrast agents do not affect the quantitative accuracy of PET following attenuation correction
(SST15-05 ), 97th Scientific Assemble and Annual Meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), December 2011 (talk)
Jegelka, S.
Cooperative Cuts: a new use of submodularity in image segmentation
Second I.S.T. Austria Symposium on Computer Vision and Machine Learning, October 2011 (talk)
Lois, C., Bezrukov, I., Schmidt, H., Schwenzer, N., Werner, M., Pichler, B., Kupferschläger, J., Beyer, T.
Effect of MR Contrast Agents on Quantitative Accuracy of PET in Combined Whole-Body PET/MR Imaging
2011(MIC3-3), 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference (NSS-MIC), October 2011 (talk)